06 - Create a SQL database (5 min)
In this walkthrough, we will create a SQL database in Azure and then query the data in that database.
Task 1: Create the database
In this task, we will create a SQL database based on the AdventureWorksLT sample database.
-
Sign in to the Azure portal at https://portal.azure.com.
-
From the All services blade, search for and select SQL databases, and then click + Add, + Create, + New.
-
On the Basics tab, fill in this information.
Setting Value Subscription Use default supplied Resource group Create new resource group Database name db1 Server Select Create new (A new sidebar will open on the right) Server name sqlserverxxxx (must be unique) Server admin login sqluser Password Pa$$w0rd1234 Location (US) East US Click OK 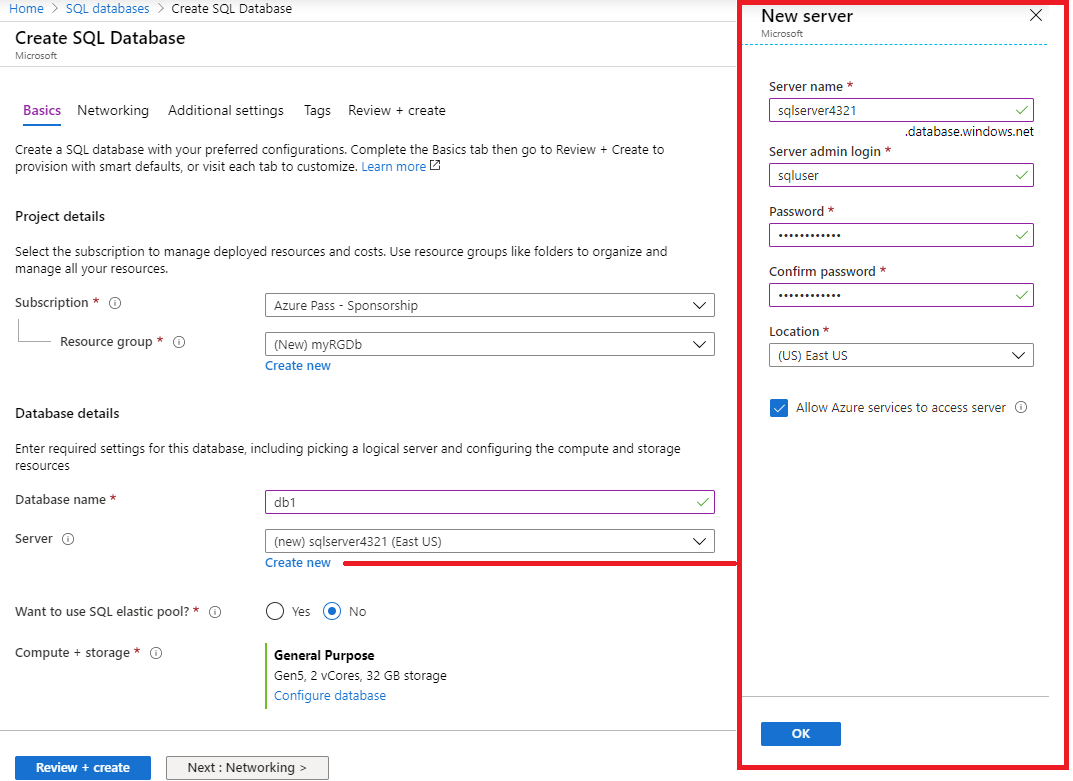
-
On the Networking tab and configure the following settings (leave others with their defaults)
Setting Value Connectivity method Public endpoint Allow Azure services and resources to access this server Yes Add current client IP address No 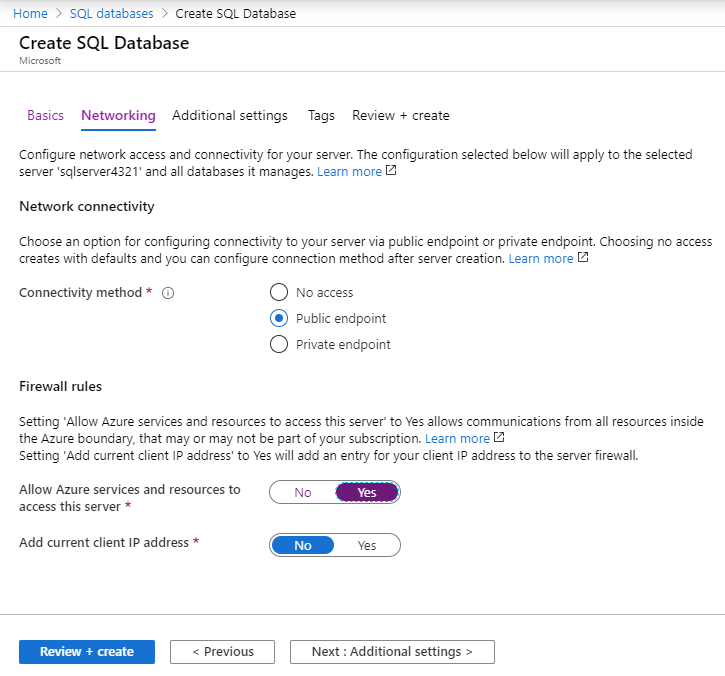
-
On the Security tab.
Setting Value Azure Defender for SQL Not now -
Move to the Additional settings tab. We will be using the AdventureWorksLT sample database.
Setting Value Use existing data Sample 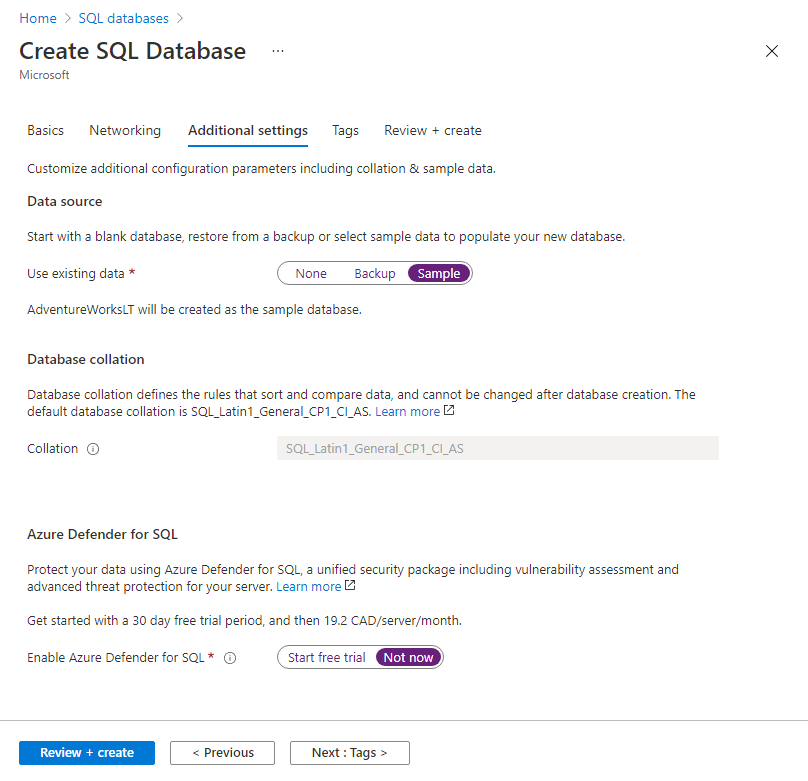
-
Click Review + create and then click Create to deploy and provision the resource group, server, and database. It can take approx. 2 to 5 minutes to deploy.
Task 2: Test the database.
In this task, we will configure the SQL server and run a SQL query.
-
When the deployment has completed, click Go to resource from the deployment blade. Alternatively, from the All Resources blade, search and select Databases, then SQL databases ensure your new database was created. You may need to Refresh the page.
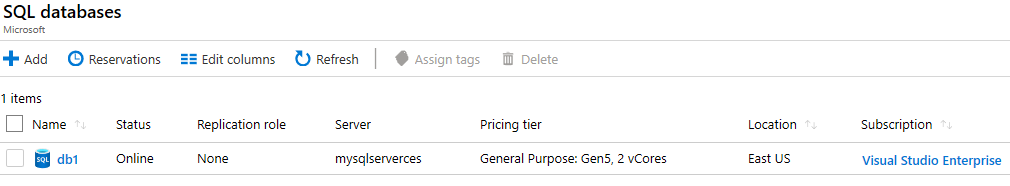
-
Click the db1 entry representing the SQL database you created. On the db1 blade click Query editor (preview).
-
Login as sqluser with the password Pa$$w0rd1234.
-
You will not be able to login. Read the error closely and make note of the IP address that needs to be allowed through the firewall.
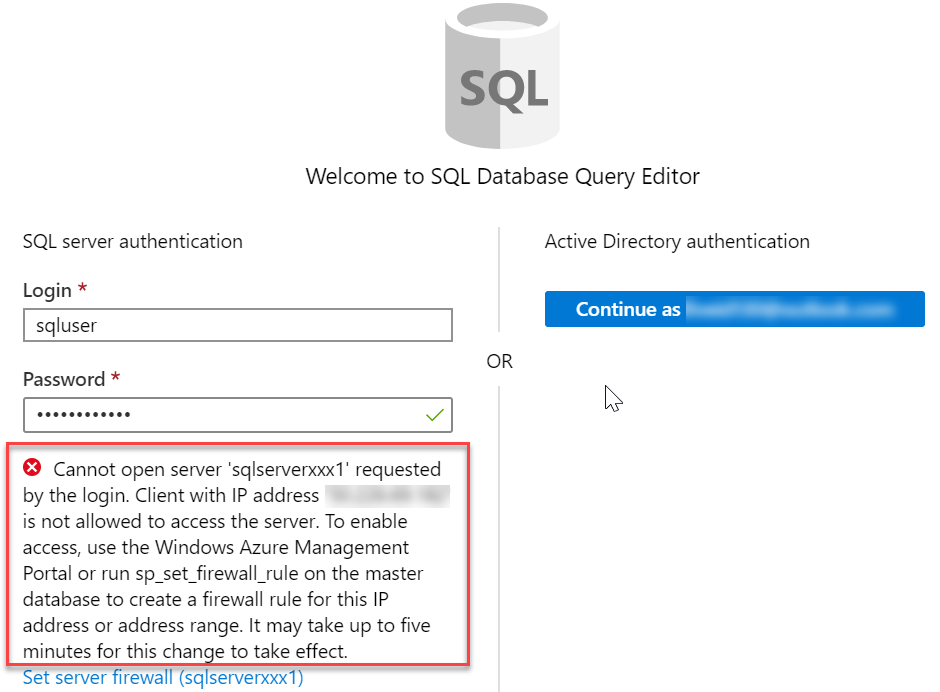
-
Back on the db1 blade, click Overview.
-
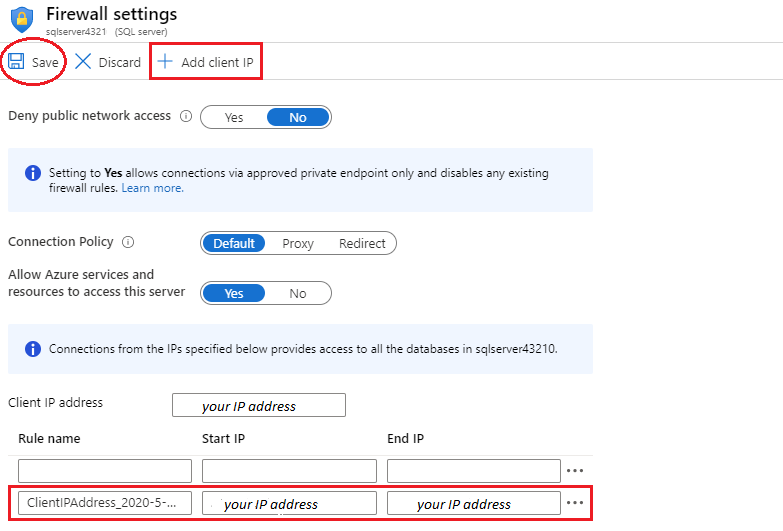
From the db1 Overview blade, click Set server firewall Located on the top center of the overview screen.
-
Click + Add client IP (top menu bar) to add the IP address referenced in the error. (it may have autofilled for you - if not paste it into the IP address fields). Be sure to Save your changes.
-
Return to your SQL database (slide the bottom toggle bar to the left) and click on Query Editor (Preview). Try to login again as sqluser with the password Pa$$w0rd1234. This time you should succeed. Note that it may take a couple of minutes for the new firewall rule to be deployed.
-
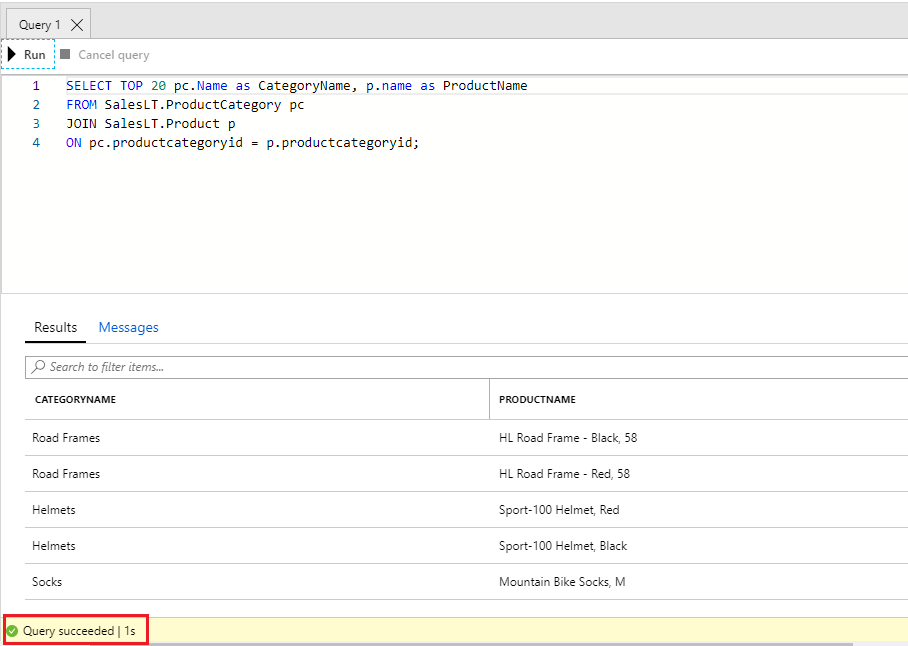
Once you log in successfully, the query pane appears. Enter the following query into the editor pane.
SELECT TOP 20 pc.Name as CategoryName, p.name as ProductName FROM SalesLT.ProductCategory pc JOIN SalesLT.Product p ON pc.productcategoryid = p.productcategoryid;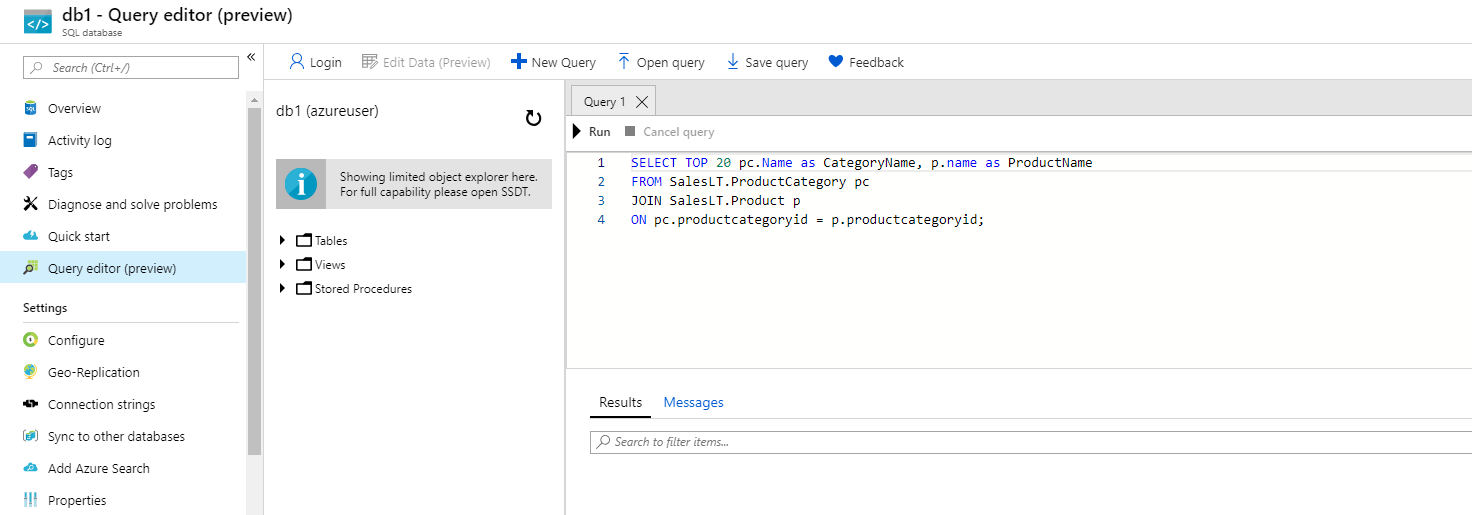
-
Click Run, and then review the query results in the Results pane. The query should run successfully.
Congratulations! You have created a SQL database in Azure and successfully queried the data in that database.
Note: To avoid additional costs, you can remove this resource group. Search for resource groups, click your resource group, and then click Delete resource group. Verify the name of the resource group and then click Delete. Monitor the Notifications to see how the delete is proceeding.